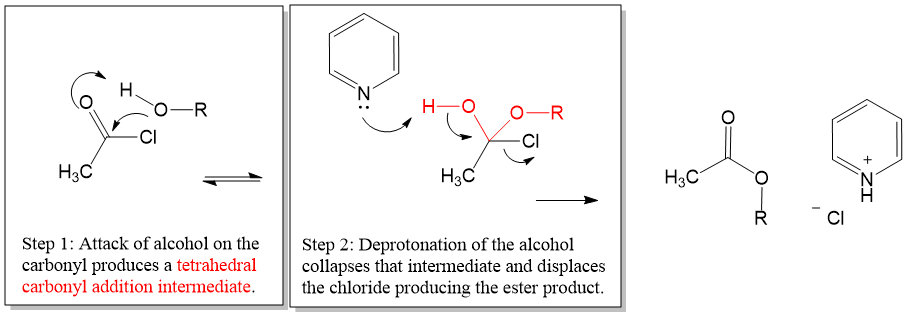
Here is a look at a reaction directly from our proven organic chemistry flash card system:
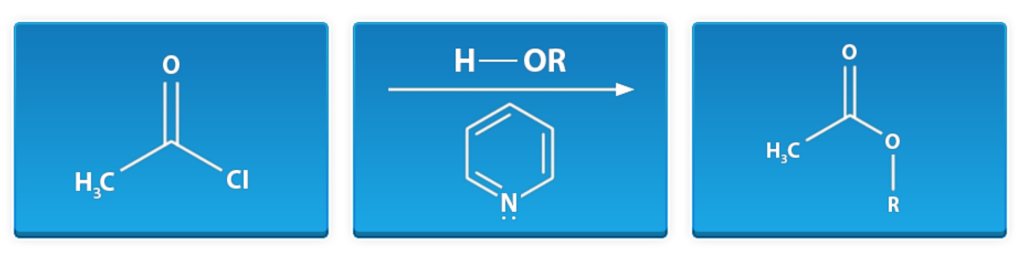
Esterification of Acid Chloride
Overall Big Picture: In this reaction, an acid halide is reacted with an alcohol to give an ester.
Acid Chloride + Alcohol → Ester
Key Tip: A mild base is required to drive the reaction forward.
Key Comparison: This reaction is only possible due to the high reactivity of acid halides for nucleophiles, even weak ones like alcohols.
Mechanism Hint: Collapse of the addition intermediate is propagated by deprotonating by pyridine, which helps to drive the reaction forward.
Note: When this reaction is carried out using p-toluensufonyl chloride (tosyl group), this reaction is a good protecting group for alcohols.
First window: acetyl chloride
Middle window: alcohol, pyridine
Last window: methyl ester